Why was the study done?
The objective was to evaluate the profitability of two vaccines against M. haemolytica by studying production parameters in a lamb feedlot.
The parameters compared were: average daily gain (ADG), mortality, feed conversion rate (FCR) and number of animals in the sick pen.
How was it done?
The study was conducted in a lamb feedlot in Baza, in the south of Spain. A total of 440 lambs with an average weight of 25 kg upon entering the feedlot were included, and they were separated into two groups:
– Group A: vaccinated with a leukotoxoid-based vaccine (Pasterbact®).
– Group B: vaccinated with a M. haemolytica bacterin-based vaccine (vaccine B).
The study lasted 76 days and the following were recorded:
– average weight of each group every 10-11 days
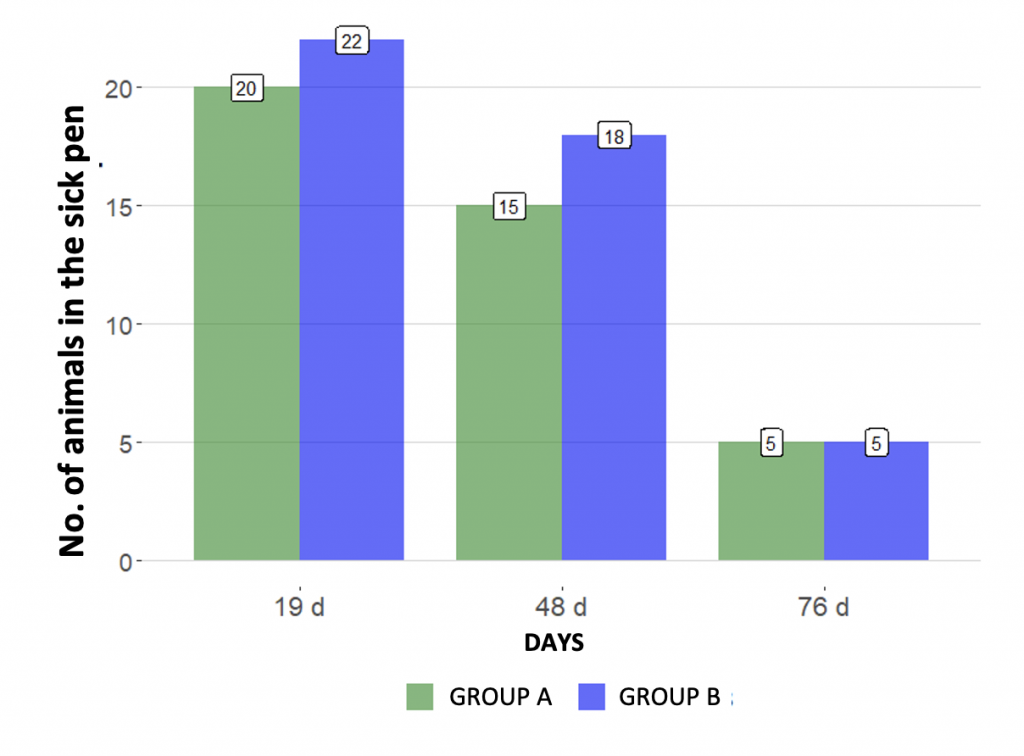
– number of animals in the sick pen
– number of deaths
In addition, the return on investment (ROI) of Pasterbact® was calculated.
Results obtained
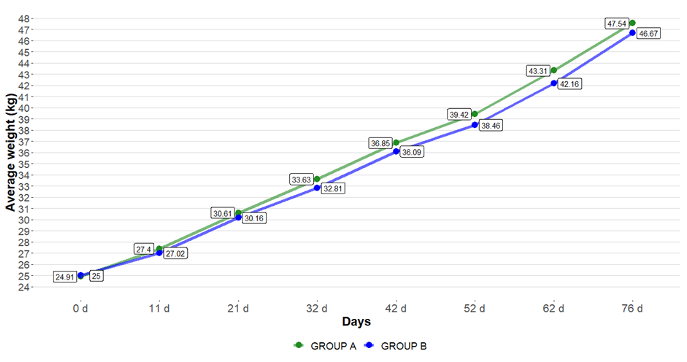
The results showed a higher final average weight and average daily gain in Group A. Regarding the feed conversion rate, it was lower in this group than in group B.
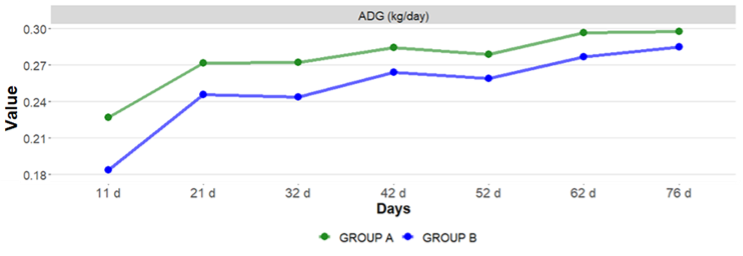
The group vaccinated with Pasterbact® showed better production parameters.
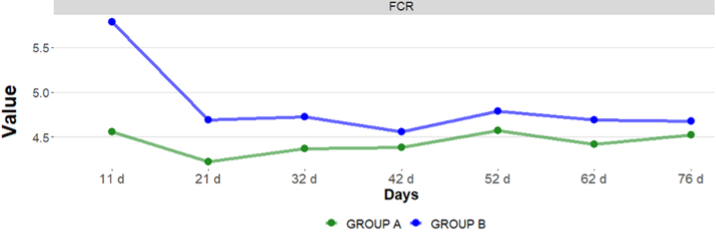
Regarding morbidity and mortality, the Pasterbact® vaccine demonstrated a reduction of 12% and 50%, respectively, compared to vaccine B.
Finally, the economic study taking into account the extra cost of Pasterbact®, resulted in an ROI of 1:10.7.
What can we conclude?
With the Pasterbact® vaccine, based on leukotoxoid, we can obtain:
– Better production parameters (ADG, FCR)
– Better lamb health
– Better profitability
Pasterbact® has been shown to reduce the impact of ORC in lamb feedlots
Article written by:
Tania Peralvarez Puerta. Global Product Manager, Small Ruminants Franchise – HIPRA