Why is the One Health concept important?
The inappropriate use of antibiotics can contribute to the development of resistant bacteria , which multiply and can even spread.
A link has been observed between the occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in humans and the use of antibiotics in animals, so we can deduce that transmission is possible.
The problem of resistance needs to be tackled using a “One Health” approach.
Numerous studies show that resistant bacteria can spread into ecological niches through various interactions between humans, animals and the environment.
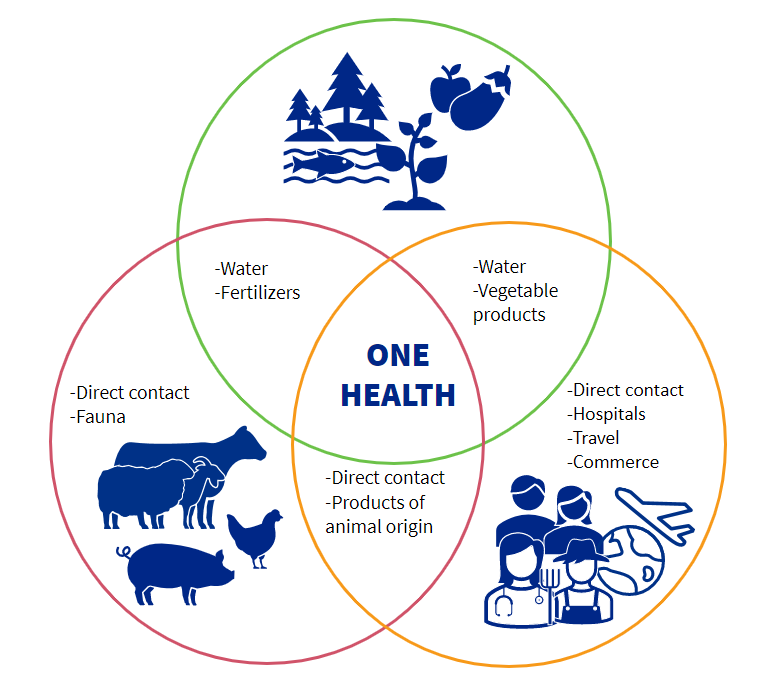
Everything is connected
Resistance can be transmitted in several ways:
Between humans:
Resistant bacteria spread easily in society. They can be transmitted by direct or indirect contact, such as surface contamination. Hospitals are “hot spots” for their spread. These bacteria can be transmitted between patients, healthcare personnel and visitors.
It is key that all healthcare professionals prescribe antibiotics adequately.
Tourism and international trade are also an important route of propagation.
Between animals:
The use of antibiotics in animals, especially if used for inappropriate means such as prophylaxis or as growth factors can lead to the appearance of resistant strains. It is very easy for them to spread through the herd and/or farm and subsequently to other species.
Animals and humans:
By direct contact, or through products of animal origin such as meat, eggs, milk, etc.
From animals to the environment:
Crops can be contaminated by the use of manure as fertiliser, and also through farm slurry water.
Environment and humans:
Resistant bacteria can be transmitted to humans by eating vegetables and fruit from contaminated crops. In addition, resistance genes can be transmitted to the normal intestinal flora.
Resistant bacteria can also be found in rivers and water reservoirs and remain even after treatment in water treatment plants.
Conclusions
● Human, animal and environmental health are closely related.
● Collaboration between various disciplines (veterinarians, doctors, researchers, biologists, etc) is necessary to combat antimicrobial resistance.
● Strategies should be established to reduce the use of antibiotics, including vaccination.
Article written by:
Tania Perálvarez Puerta. Product Manager Small Ruminants Unit – HIPRA