GENERAL OVERVIEW
At flock level for small ruminant mastitis, it is common to isolate one ‘major’ pathogen in terms of frequency (among all mastitis cases occurring during the campaign). There are two reasons for this peculiar epidemiological feature (not shared by dairy cows): first, the majority of bacteria are ‘contagious’ (Staphylococci, Mycoplasmas, some Streptococci, etc.) and/ or lamb-mediated (Pasteurellaceae, Staphylococci, etc.), and second, production is highly synchronized (concomitance of susceptibility periods).
The common existence of one major pathogen is a key issue when implementing control programmes for both vaccination and general preventive management.
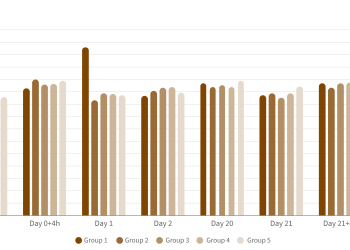
The incidence of clinical mastitis in goats and ewes is usually below 5–7% per year (this percentage may be underestimated as some breeders do not record mild chronic mastitis). This average value may be considered a technical goal for dairy herds to achieve.
“S. aureus is the most common cause of Clinical mastitis”
MAIN CLINICAL MASTITIS PATHOGENS
Among the main causative agents of these sporadic clinical IMI (Intramammary infections), Staphylococcus aureus is the most common. Any breeder knows the typical clinical form of S. aureus mastitis: the so-called ‘gangrenous’ mastitis, which should be referred to as necrotic mastitis (‘blue-bag’ for English-speaking meat sheep breeders).
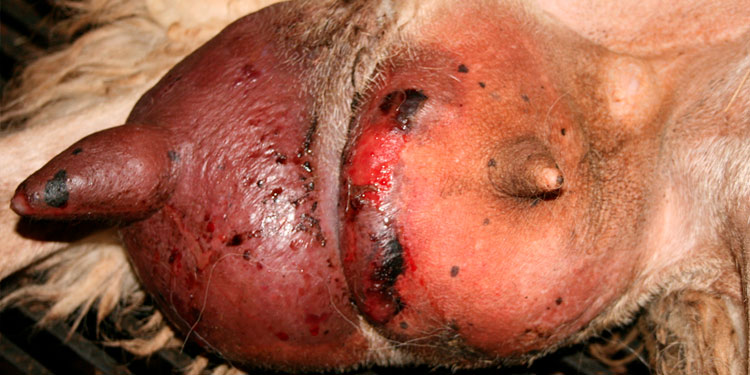
Other significant causative organisms of sporadic clinical mastitis are coagulase-negative Staphylococci (CNS), Streptococci, coliforms and coryneforms. In the case of suckling ewes (or goats), Mannheimia haemolytica has also been isolated.
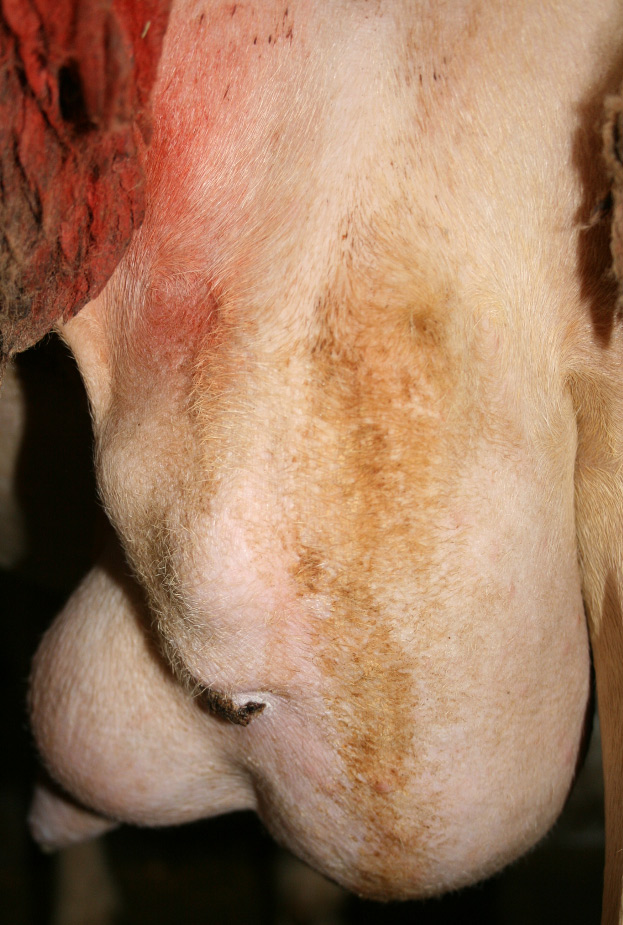
These main bacterial groups aetiologically characterize the ‘normal’, baseline situation of flocks with no outbreaks (Bergonier et al., 2003). When the epidemiological situation deteriorates, the herd experiences a sudden epizootic outbreak (incidence generally increases within the 3 first months of lactation), or an enzootic condition with usual recurrences at the beginning of each dairy campaign (young animals).
“Clinical cases generally take place during the 3 first months of lactation”
References:
Adapted from Ovipedia Article created by Dominique Bergonier, DVM, Dipl. ECAR, Dipl. ECSRHM, Professor and Researcher at the National Veterinary School (ENV Toulouse) and INRA (France).