Ovine enzootic abortion (OEA) was first reported in Scotland in 1936. Since then, the scientific community has been studying the behaviour of this bacteria. The goal is to set up a strategy to control and prevent this disease and reduce its economic impact. Here, you will find out what you need to do and what you must not do to control it.
Three types of measures have been established in the control and prevention of OEA:
MANAGEMENT MEASURES
These consist of preventing the transfer of animals without serological control, preventing contact of pregnant ewes with infected placentas or foetuses and keeping healthy flocks away from infected flocks.

These measures are not enough, given the difficulty of isolating the infected animals.
“Management measures are critical to controlling OEA and must be combined with vaccination“
USE OF ANTIBIOTICS
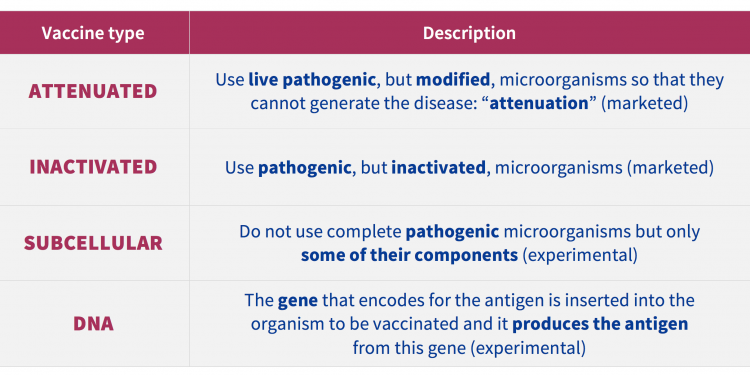
This type of measure, in the control of a C. abortus infection, is highly influenced by the intrinsic condition of chlamydia, such as obligate intracellular bacteria.

Thus, despite being a bacterium sensitive to many antibiotics, high concentrations of the bacteria in blood are required in order to achieve successful therapeutic outcomes.
“Antibiotic therapy is economically unsustainable and unsuccessful”
This, along with the difficulty of predicting the time of the infection, makes the use of these measures, for certain periods of the pregnancy, economically unsustainable, and the inappropriate use of antibiotics could cause the infection to sub-clinically persist in the animal or the possible risk of developing resistance to antibiotics.
“The use of antibiotics does not help in controlling OEA: infected animals will continue shedding and spreading the infection in the flock”
CONTROL ENZOOTIC ABORTION WITH VACCINATION
Active immunisation: the adequate vaccination of animals could control chlamydial abortion in sheep, given that the first exposure of small ruminants to C. abortus induces a protective immunity preventing reproductive problems after contact with this infectious agent.
“Vaccination is the best way of controlling OEA”
For this reason, vaccination is the most effective and important way of controlling and preventing enzootic abortion.
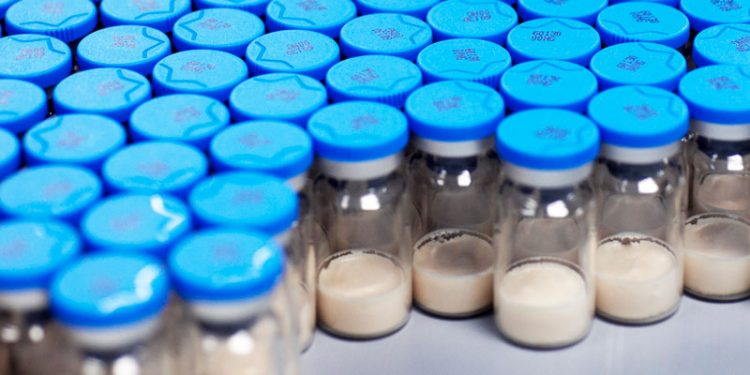
At present, the main types of vaccines that have been developed, commercially or experimentally, against this disease are as follows:
Article written by:
María Rosa Caro, Jesús Salinas and Nieves Ortega, Department of Animal Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Murcia. 30100 Murcia, Spain.