Current situation and future outlook
Currently, an increase in animal production has been observed, and this implies the growth of animal censuses. Moreover, systems are increasingly intensive, and the use of antibiotics to guarantee health and productivity is a common practice.
These habits mean that, globally, 73% of antibiotics are used in production animals . If we fail to implement measures in the short term, these figures will increase, because the demand is becoming higher.
By 2030, the use of antibiotics in animals is estimated to increase by 67% and 105,600 tonnes will be used.
Map of antibiotic consumption
There is a high level of geographic variability in the consumption of antibiotics. There are countries that use large quantities, and some of them are expected to further increase consumption. These differences between countries depend, to a large extent, on whether proper use is made.
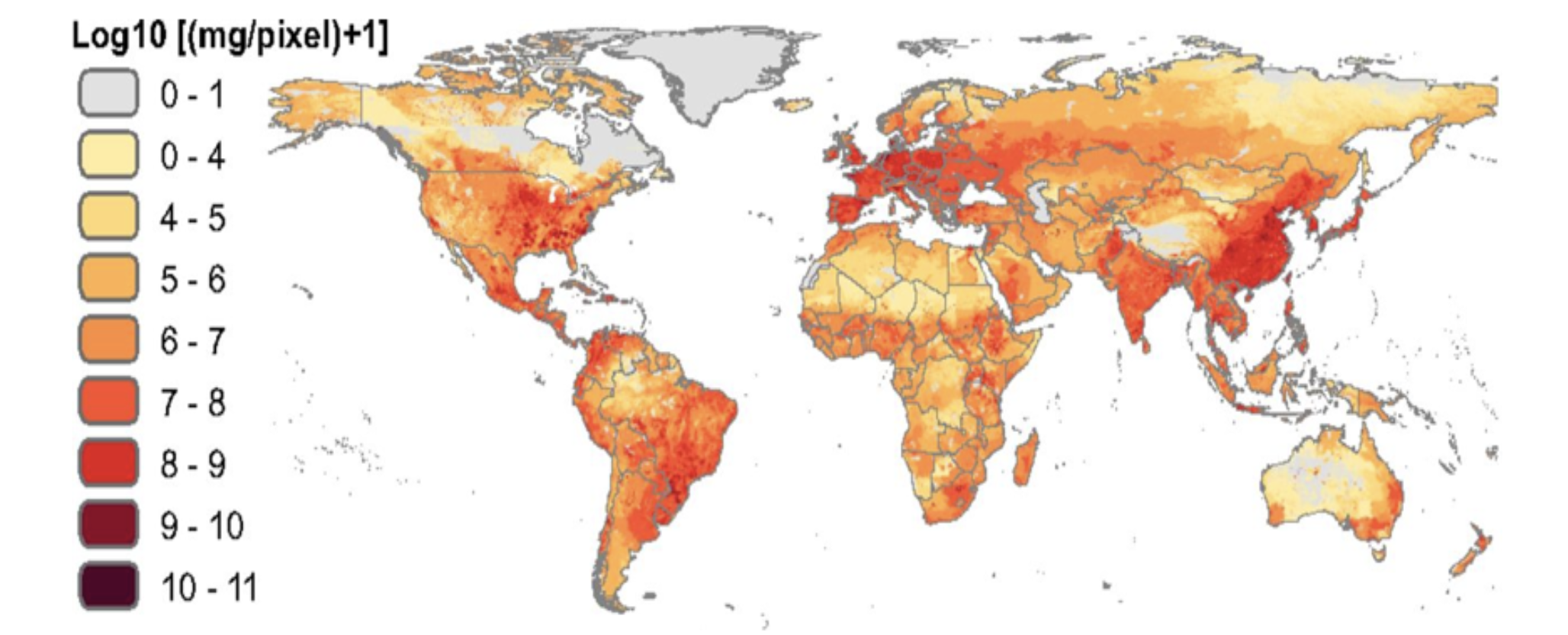
Certain geographic patterns can be observed. There are “hot spots”, such as eastern China, countries in South-East Asia, India, southern Brazil, Mexico, various areas of the United States, and a large part of Europe.
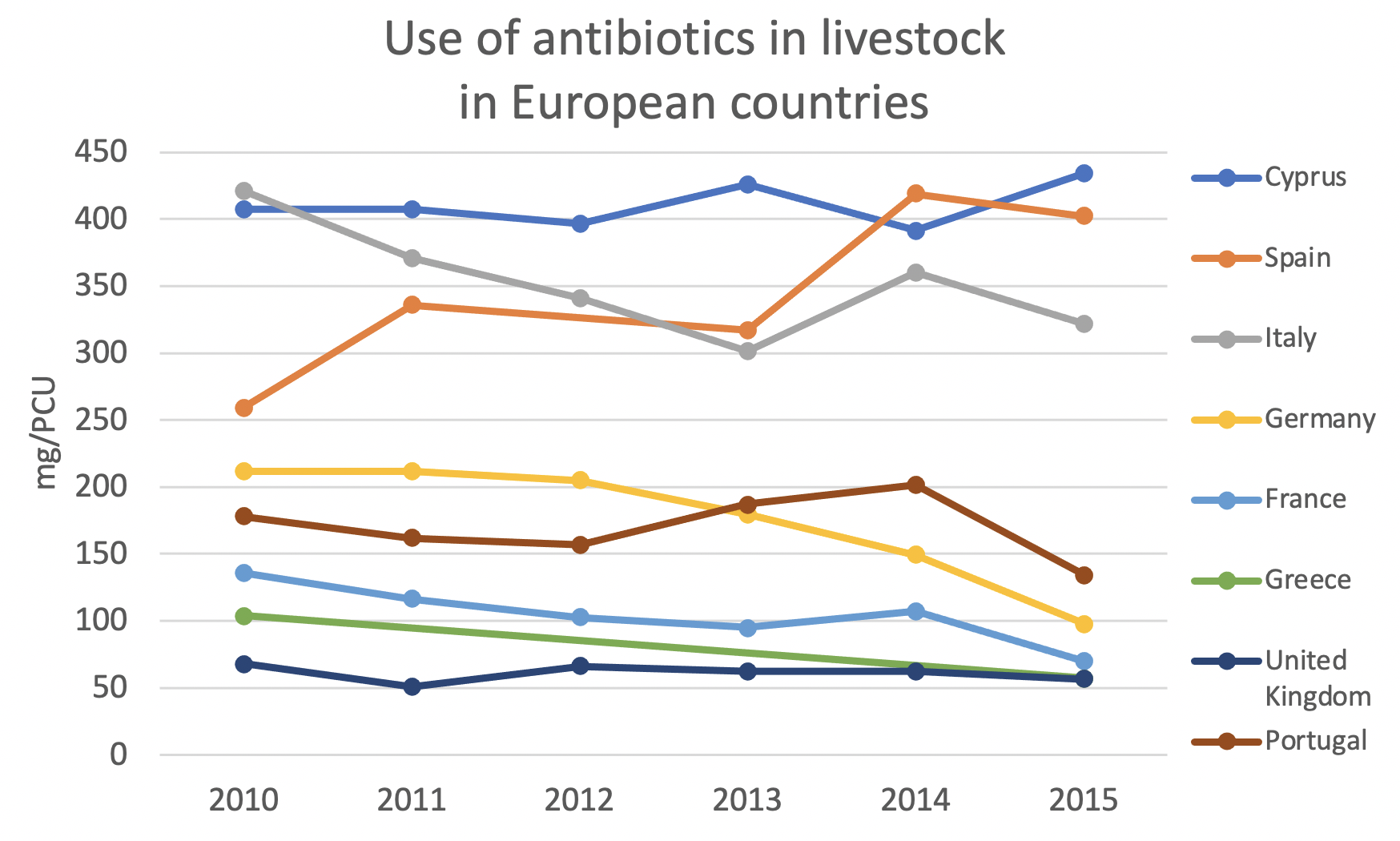
If we focus on Europe, we can see different trends between countries. Many of them have already experienced a decrease in antibiotic use. The objective in the EU is to continue to promote the prudent use of antibiotics and disease prevention to reduce antibiotic use in all countries.
Consequences of the unnecessary use of antibiotics
In veterinary practice, antimicrobials are used to treat infectious disease, but also erroneously as prophylaxis or growth factors.
Inappropiate habits of antibotic use facilitate the emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic resistance rates in animals are increasing exponentially, putting animal and human health at risk. According to the WHO, resistance is now a major problem worldwide, causing 700,000 deaths annually. In 2050, resistance could cost the lives of up to 10 million people.
The WHO has declared antimicrobial resistance a major threat to public health.
Conclusions
● The unnecessary use of antibiotics fosters the emergence of antimicrobial resistance.
● This resistance is a threat to global health.
● Preventive measures , such as vaccination, need to be implemented to reduce the use of antibiotics.
Article written by:
Tania Perálvarez Puerta. Corporate Product Manager, Small Ruminants Unit – HIPRA