When did it all start?
The first evidence that we have of their use was in China 2,500 years ago, where they were aware of the therapeutic properties of mouldy soybean curds. In ancient Egypt and Greece moulds and plants were also used to treat infections.
“In ancient times, moulds and plants that produced antibiotic substances were used.”

Modern uses of antibiotics
The first clinical use of antibiotics was in the 1890s, with the discovery of pyocyanase by Emmerich and Löw. It was obtained from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and it was used to treat cholera and typhus, albeit with questionable efficacy and safety.
In 1909, Paul Ehrlich began using Salvarsan, a drug produced from arsenic that was effective at treating syphilis.
“The first antibiotics used in clinical practice weren’t very effective or safe.”
A chance discovery
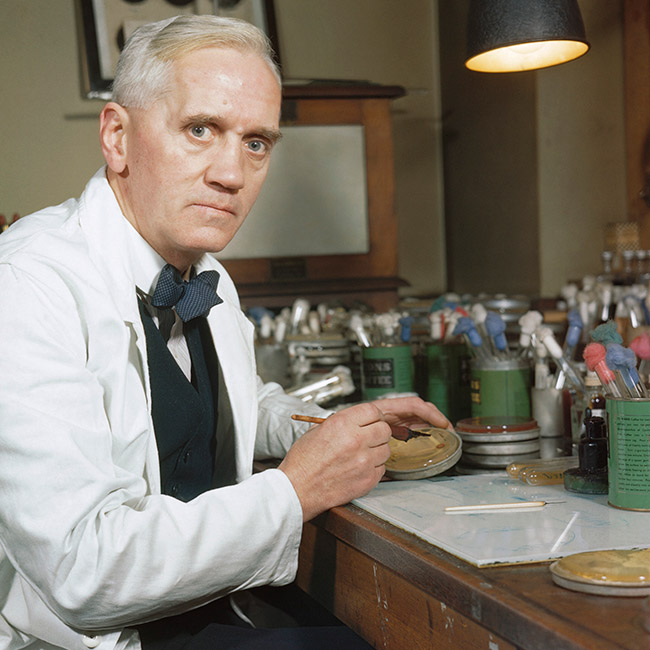
Alexander Fleming was known both for his intelligence and his carelessness. In 1928, some of his microbial cultures were contaminated with moulds, and he observed that there was no bacteria in the area surrounding them.
He identified the fungi as Penicillium and named the substance it produced penicillin.
“Fleming observed that there was no bacterial growth around the Penicillium.”
However, it wasn’t until the Second World War that penicillin started to be produced on a large scale to treat illnesses.
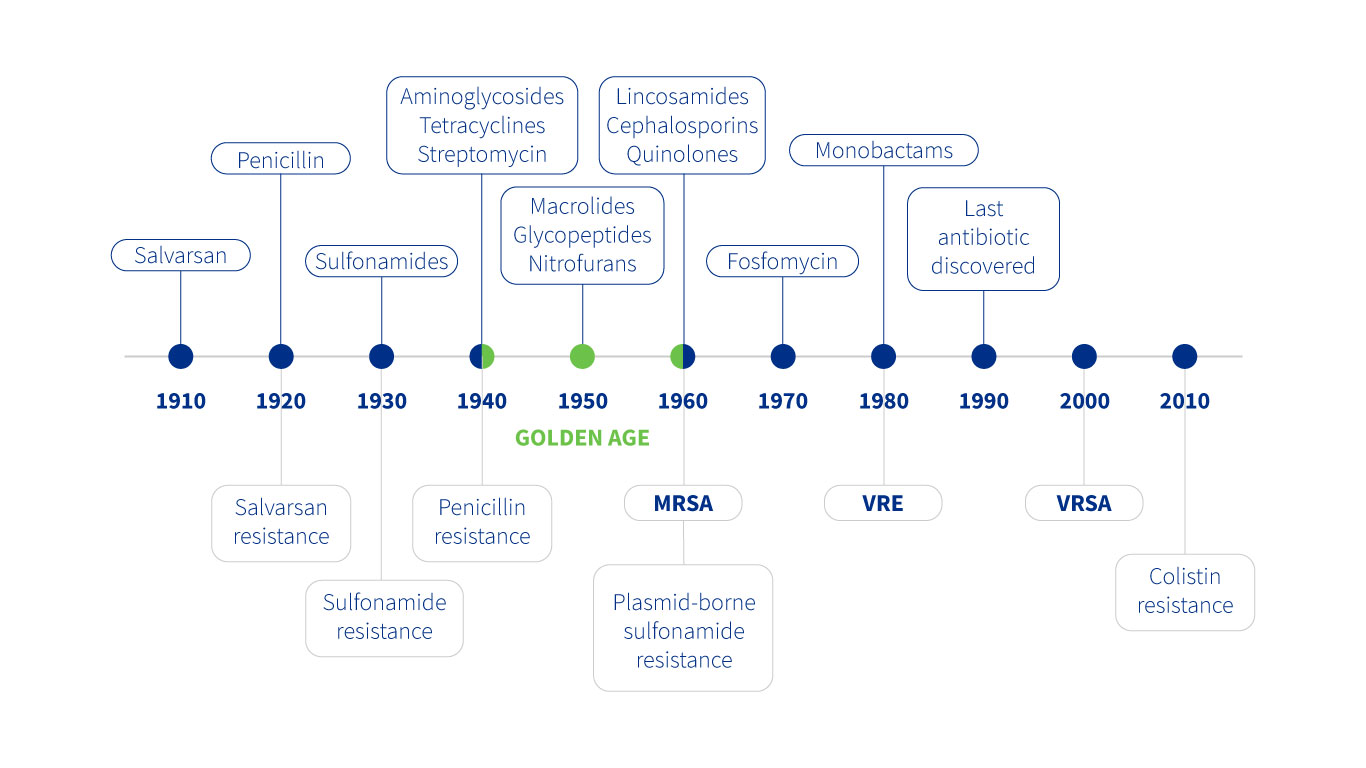
Evolution up to the present day: Golden Age of antibiotics
The 1940s were the Golden Age of antibiotics. A wide range of types were discovered in a short period of time and they were used excessively.
This uncontrolled use led to the development of resistance, putting their effectiveness at risk.
“Following the discovery of penicillin, there was a surge in the search for and use of new substances.”
It has been several decades since a new antibiotic was discovered, and as a result, multidrug-resistant bacteria are an increasing cause of death.
How have antibiotics helped humanity?
Antibiotics have made it possible to:
● Treat infectious diseases that were previously fatal.
● Further develop medical specialities.
● Develop procedures such as surgery, transplants and cancer treatments.
● In veterinary science, they have helped to treat sick animals, improve their growth and serve as prophylaxis.
“The development of antibiotics represents the most significant medical breakthrough of the 20th century.”