Staphyloccoci…the cause of a serious problem!
Amongst all the problems that we can find on farms, mastitis in sheep and goats is normally the one that farmers and vets are most concerned about, for two main reasons: its economic impact and the difficulty in controlling it.
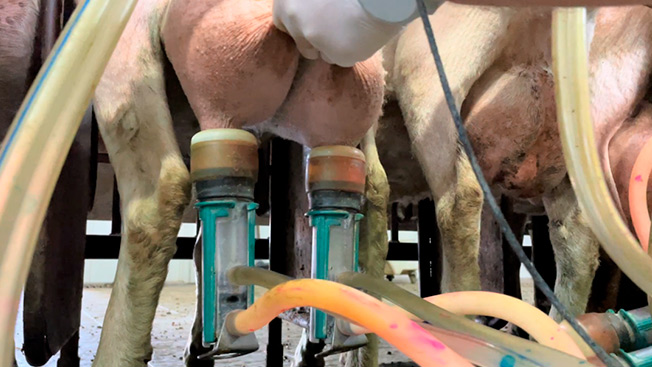
Staphyloccocus aureus and CNS are the most prevalent pathogens causing both clinical and subclinical mastitis cases.
“Staph aureus and CNS, the main causes of clinical and subclinical mastitis”
A group of scientists performed two field investigations throughout Greece to associate the staphylococcal populations with the use of anti-staphylococcal mastitis vaccines.
How was it done?
Samples were taken from the teatcups (upper and lower part) to confirm the shedding of staphylococci.
A total of 1418 samples were collected from 333 farms (255 sheep and 66 goat farms respectively) that were involved in the cross-sectional study.
What was isolated?
The results of these studies confirmed that these staphylococci are very often circulating on small ruminant farms, becoming a great threat to the sector.
Proportion of contaminated teatcups
Of the total number of samples collected, 23% were infected; the presence of staphylococci was confirmed on 41.2% of the sheep farms; and it was even higher for the goat herds, 53%.
“Staphylococci were found on over 50% of dairy goat farms”
Different staphylococcal species were isolated but the majority were biofilm-forming staph, 87.4%; there was no difference in isolates from sheep and goat farms in the study.
“Over 87% of staphylococcal species isolated were the biofilm-forming type”
Biofilm-forming strains of staphylococci are more resistant to antibiotic treatment and immune system cells, which helps the bacteria to attach on to the teatcups and survive the unfavourable conditions.
Different types of vaccines…different impact!
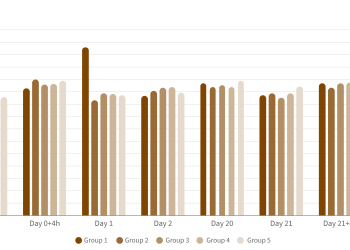
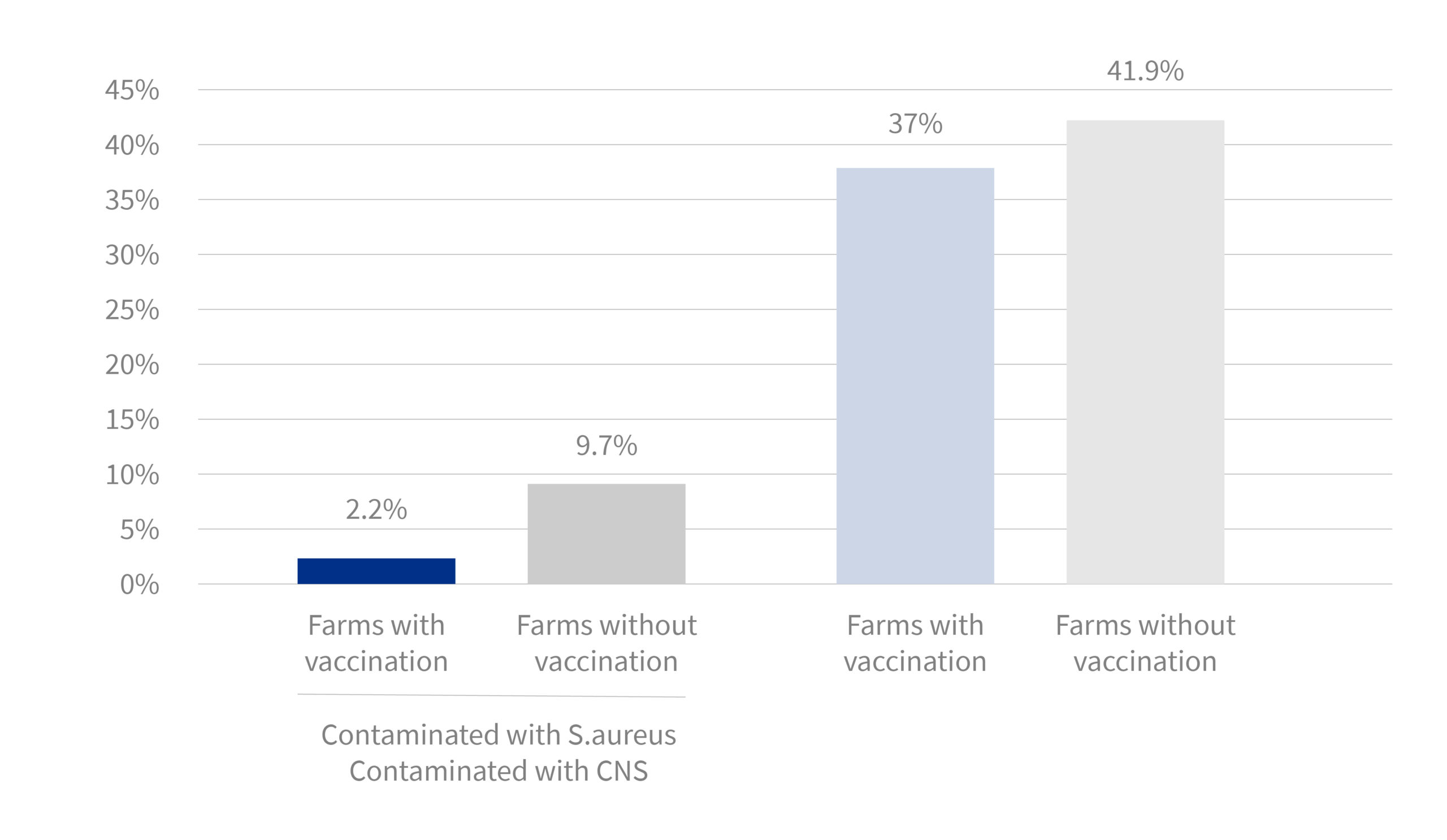
In the cross-sectional study, three commercial vaccines were used on some farms (42%); fewer contaminated teatcups were found on vaccinated farms in both studies.
Effect of vaccination in the proportion of contaminated teatcups
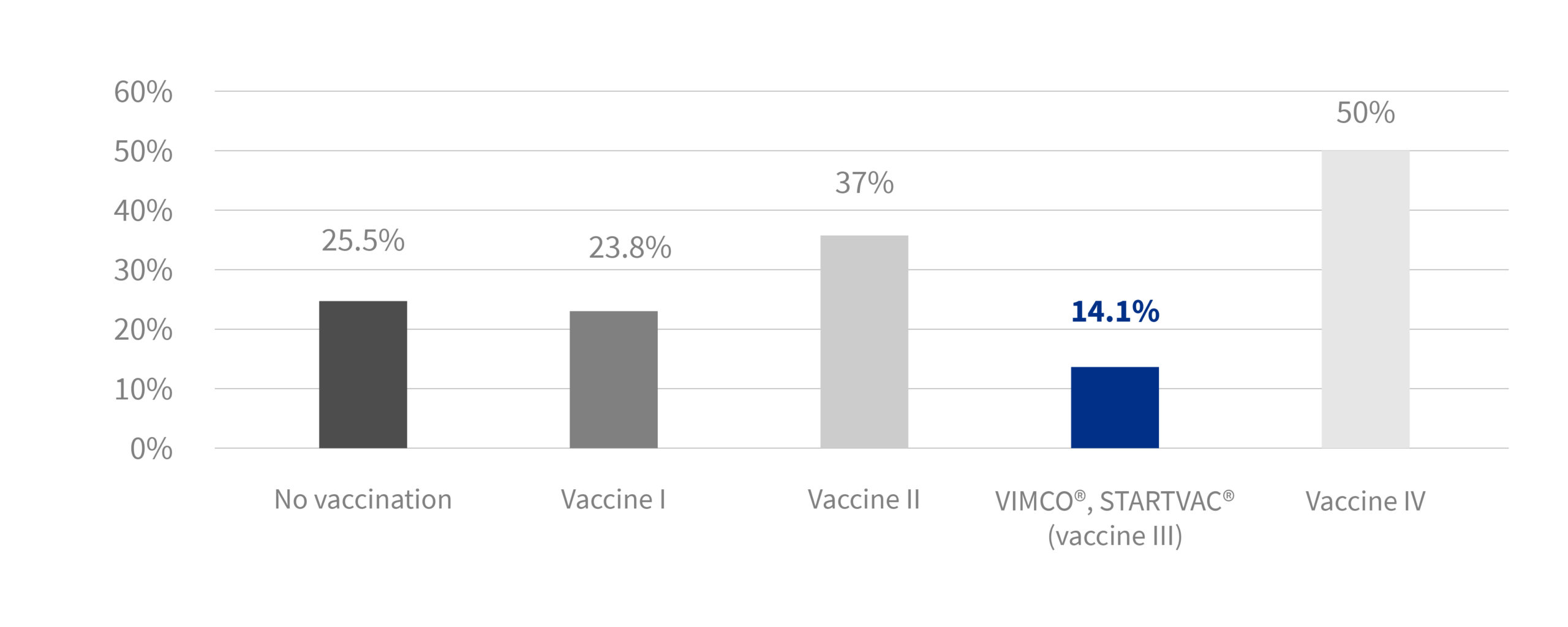
These results suggest that vaccination against mastitis reduces shedding, which is crucial to the control of mastitis on sheep and goat farms.
“Farms vaccinated with VIMCO® or STARTVAC®: biofilm-forming staphylococci isolated in only 10.9% of teatcups”
Farms on which vaccine against antibiofilm-forming was used, showed a greater reduction in contaminated teatcups than farms where other commercial vaccines were used or unvaccinated farms: 12.1% vs 25.1%.
Conclusions
● The majority of staphyloccoci isolates were biofilm-forming staphylococci.
● Anti-staphylococcal mastitis vaccination reduces the spread on farms.
● VIMCO® and STARTVAC® showed a higher reduction of shedding than other mastitis vaccines.
ACCESS TO THE PEER REVIEWED ARTICLE
Authors of the study: