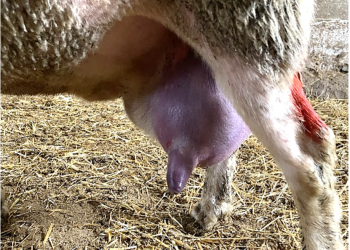
Chlamydia abortus is one of the pathogens that causes the most reproductive problems in sheep and goats. Even though it is highly prevalent, there are still unknowns about its cycle. Having a good understanding of the disease is of great importance for implementing the correct control measures.
Infection “pattern”
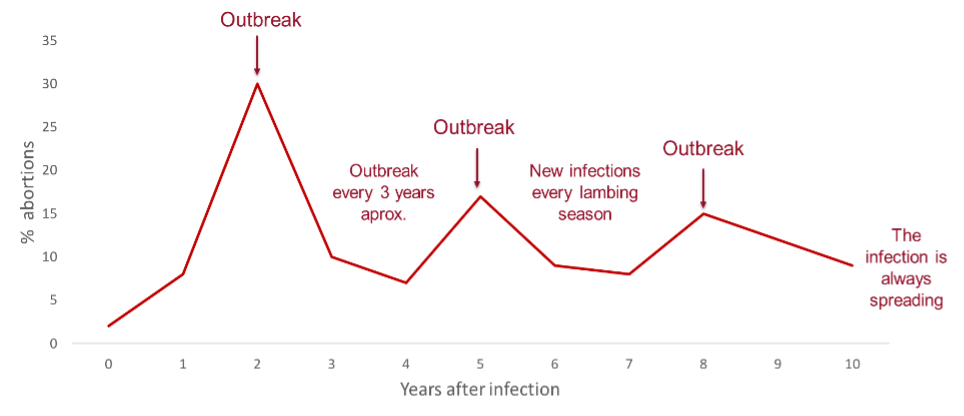
When a herd is infected by C. abortus, the disease behaves as follows:
First year: there is usually a low number of abortions. Only animals that become infected when they are at the beginning of pregnancy will abort, and they will also be a source of infection.
Infected animals that are not pregnant or are in advanced gestation (>110 d) show no signs, since chlamydia will remain latent until the next pregnancy.
Second year: an outbreak or “abortion storm” usually occurs, as many more animals are infected than the first year. This is because the animals that aborted the previous year were excreting chlamydia, spreading the infection throughout the herd.
Furthermore, in animals with latent infection, Chlamydia reactivates the cycle when they become pregnant again, causing abortion.
The second year after C. abortus infection, an outbreak occurs with an abortion rate of 20-30%
Third year: the infection stabilizes and the abortion rate is usually around 5-10%. However, Chlamydia is also excreted in normal deliveries, so the infection continues to spread.
Following years: an outbreak may appear approximately every 3 years. This is because animals develop a natural immunity that protects them from aborting for only 1-3 years.
Fig 1. Estimation (hypothetical case) of how the % of abortions evolves in a naïve herd infected with Chlamydia abortus.
Point of Control
The excretion of chlamydia is the factor that determines its spread throughout the flock and the dynamics of the infection.
Therefore, the reduction of excretion will be the key point for its control, and we can achieve this with vaccination.
The results of a study show that the inactivated INMEVA vaccine reduces the excretion of Chlamydia by 55%.
By vaccinating the flock we will be able to, apart from reducing the number of abortions, reduce the infection pressure and protect the animals from new infections.
Conclusions
It is important to know how the disease occurs in order to control it.
The key point for the control of C. abortus is reducing excretion, and we can achieve this with vaccination.
Article written by:
Tania Perálvarez Puerta. Global Product Manager, Small Ruminants Franchise – HIPRA
References:
Montbrau, C. et al., (2020) Evaluation of the Efficacy of a New Commercially Available Inactivated Vaccine Against Ovine Enzootic Abortion. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 7(593)
Milne, E. et al., (2008) Epidemiological modelling of chlamydial abortion in sheep flocks. Veterinary Microbiology 135 (2009) 128–133
Longbottom, D. et al., (2013) Intranasal Infection with Chlamydia abortus induces dose-dependent latency and abortion in sheep. Plos One 8(2)
Livingstone, M. (2008) Molecular detection of Chlamydophila abortus in post-abortion sheep at oestrus and subsequent lambing. Veterinary Microbiology 135 (2009) 134–141